Comprehensive Design for a Fencing Project: A Step-by-Step Approach
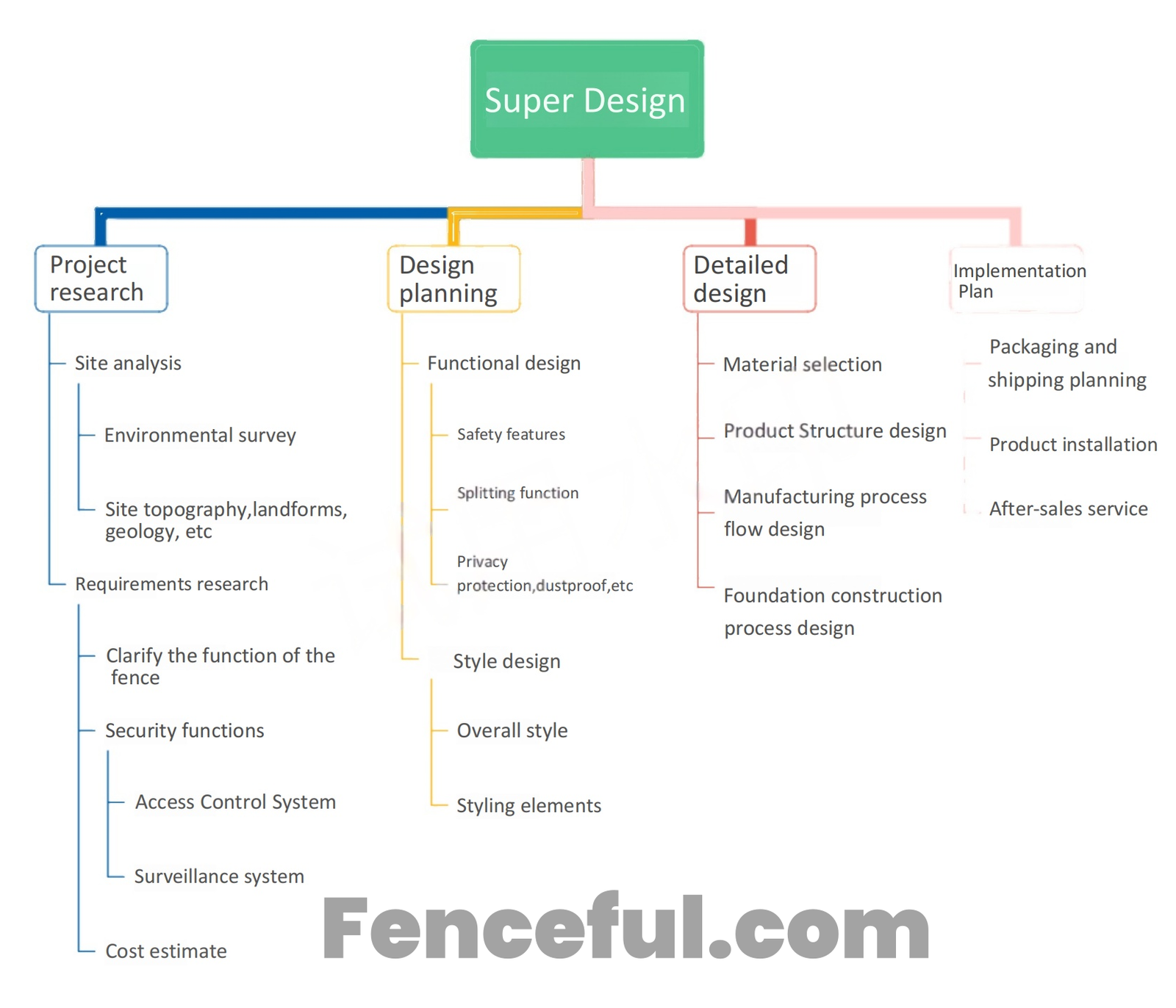
Fencing projects, whether for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes, require a detailed and strategic design process to ensure safety, functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Below is a thorough guide to the stages involved in a successful fencing project, from initial research to post-installation service.
1. Research and Planning
Research
The success of any fencing project starts with extensive research. This phase involves understanding the purpose of the fence, the materials available, and the regulatory requirements governing its installation. Key factors such as local climate, environmental conditions, and the specific needs of the site (e.g., privacy, security, or aesthetic appeal) must be considered.
Planning
Planning forms the blueprint for the entire project. This includes defining the scope, timeline, and cost estimate. Detailed planning also involves understanding the site’s unique characteristics, such as topography and existing landforms, which can influence the type of fence to be installed and the required foundation.
2. Site Analysis and Environmental Survey
Site Analysis
Before any physical work begins, a comprehensive site analysis is crucial. This stage examines the land’s topography, geology, and other physical characteristics, such as soil quality and existing structures, which could impact the fence’s design and installation. Site analysis also includes determining the functional needs of the fence based on its location, such as security, privacy, and environmental protection.
Environmental Survey
An environmental survey evaluates the impact of the fencing project on the surrounding ecosystem. Considerations might include the potential disruption to local wildlife, plant life, or natural resources. Additionally, this survey helps to determine the necessary materials to ensure that the fence can withstand environmental factors like wind, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
3. Functional Design and Material Selection
Functional Design
In this phase, the functionality of the fence is defined. The primary functions of fencing, such as security, privacy, and access control, are addressed, ensuring the design fulfills all of the client’s needs. The design should also consider aesthetic aspects and harmonize with the surrounding landscape.
Material Selection
Material selection plays a critical role in the durability, aesthetics, and functionality of the fence. Factors like weather resistance, maintenance requirements, cost, and environmental impact should guide the selection. Materials can include wood, vinyl, metal, or composite options, each providing unique benefits based on the intended purpose of the fence.
4. Design Details and Styling Elements
Style Design
Designing the style of the fence includes decisions regarding its visual appearance, including color, texture, and overall shape. The style should be consistent with the client’s preferences while also complementing the architectural style of the surrounding structures. Whether modern, rustic, or traditional, the style design enhances the overall appeal and value of the property.
Styling Elements
Styling elements like decorative features, post caps, gates, and other ornamental additions contribute to the fence’s visual appeal. These elements allow for customization and can give the fence a unique character, while still maintaining its functional goals, such as security and privacy.
5. Security Features and Access Control
Security Functions
Fencing projects often serve as security barriers to prevent unauthorized access and protect the property. Security features include height, strength, and the integration of modern security systems. Anti-climbing devices, barbed wire, or electric fencing may be incorporated for high-security areas.
Access Control System
Access control is a crucial aspect of fencing for commercial and residential applications. Installing gates, turnstiles, or entry points equipped with automated systems such as keypads, biometric scanners, or RFID access systems ensures that only authorized individuals can enter the property. These systems can also be integrated with surveillance systems for enhanced security.
Surveillance System
For added protection, surveillance systems such as CCTV cameras and motion sensors can be incorporated into the fence design. These systems monitor the perimeter of the property and alert the owner to potential security breaches. Surveillance systems can be integrated into the overall fence design, ensuring they complement the aesthetics while enhancing the security features.
6. Detailed Product Structure and Manufacturing Process
Product Structure Design
The structure of the fence must be durable, stable, and able to withstand external forces such as wind, pressure, and potential impacts. The fence’s foundation and framework need to be designed with longevity and resilience in mind. The design of the posts, rails, and panels must account for various forces acting upon the fence over time.
Manufacturing Process
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing process begins. This includes the production of the fence components based on the chosen materials and specifications. Quality control measures ensure that all components meet required standards for safety and durability.
7. Foundation Construction and Installation
Foundation Construction
A solid foundation is critical for the stability and longevity of the fence. The type of foundation—whether it’s concrete, steel posts, or another solution—depends on the materials chosen for the fence and the conditions of the site. Proper foundation construction ensures the fence remains secure and upright over time, even in challenging weather conditions.
Product Installation
Professional installation ensures that the fence is erected safely, efficiently, and according to the design. The installation process must be carried out with attention to detail to avoid common pitfalls, such as poor alignment or inadequate post depth. Proper installation guarantees the fence’s strength and functionality for years to come.
8. Post-Installation: After-Sales Service and Packaging
After-Sales Service
After the fence has been installed, ongoing maintenance and after-sales service may be necessary to ensure its longevity. This includes periodic inspections, repairs, and updates to security systems. A comprehensive after-sales service plan helps maintain the fence’s functionality and appearance over time.
Packaging and Shipping
For large-scale fencing projects, particularly in the case of pre-fabricated panels or components, proper packaging and shipping are essential to prevent damage during transport. Components should be securely packed and labeled for easy identification during installation.
9. Cost Estimate and Budgeting
A detailed cost estimate should include all aspects of the project, from research and planning to materials, labor, and installation. The estimate should also account for any unforeseen expenses or contingencies that may arise during the project. Effective budgeting ensures that the project stays within financial constraints while delivering the desired results.
Conclusion
A fencing project involves careful planning, design, and implementation to meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. By following a structured approach—from research and site analysis to material selection, installation, and post-project support—stakeholders can ensure the successful completion of a fencing project that enhances security, privacy, and the overall value of the property.
By focusing on detailed design, security integration, and the use of high-quality materials, the resulting fence will serve its purpose effectively for many years.
